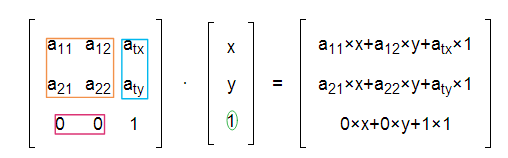To know about R-CNN let’s first know why we have to know it which is a very important thing because without a solid reason you can’t have a dedication to learn it.
R-CNN is an algorithm used for object detection in a an image. Object detection is a bit different from object recognition but this little bit difference make it a complex task for machine to tackle.
Object recognition is to check whether an image contains an object or not , it can by solved by various CNN architecture like ResNet, DeepNet, Inception-ResNet e.t.c while Object detection is a task of recognising the class of object as well as its localisation i.e where it is placed in the overall image or we can say to build a bounding box around that object in the image.
So after this you not only tell us that this is the image of a cat but also tell that where the hell it is located by building a bounding box around it.It has been used in various Automated computer vision problem like real time face detection, person tracking,pose detection e.t.c
In this Section we will discuss three types of algorithm regarding this object detection problem.
- R-CNN
- Fast R-CNN
- Faster R-CNN
R-CNN:
Introduction:
In this method we use Image segmentation method(Selective Search algorithm) to extract around 2k regions from image where probability of finding an object is high. We willn’t discuss about the segmentation method used for the region proposal rather will post a separate blog for it. we also build a thin bounding box around each (2k) regions so that to check whether the region we got is a positive example or not using IOU( Intersection over Union) technique by choosing a threshold value. If the IOU value for the proposed region is greater than the threshold with the ground truth bounding box of training example then we say that it is the positive example of that class and all the rest regions are the negative examples.It can be possible that multiple regions can have IOU value greater than threshold , all will be selected as the positive example in that case.
(**We assume here that each training example contains object of a single class only.**)
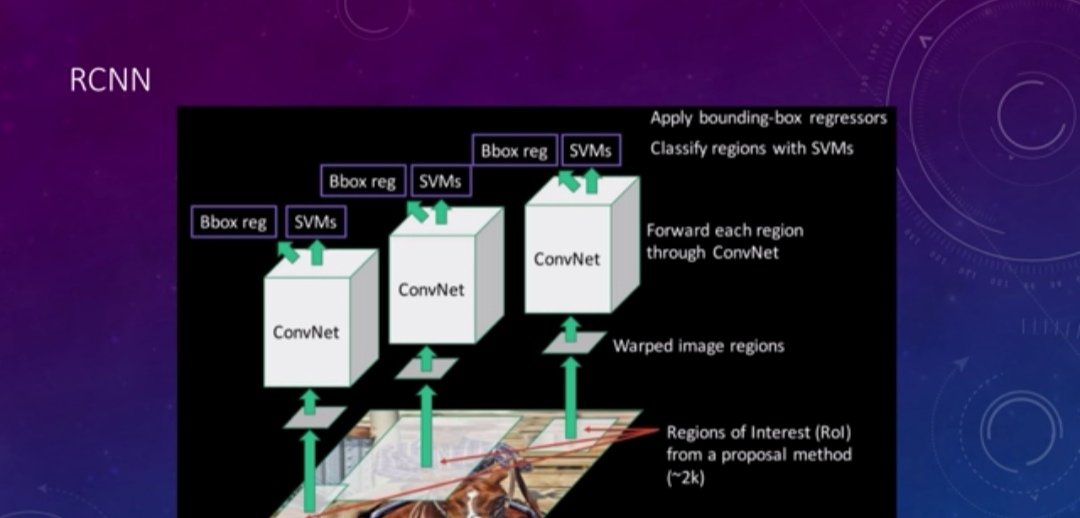
Now each region will be sent to some deep ConvNet architecture for the feature extraction process and the extracted feature vector will be sent for the SVM classifier to detect whether it contains a class or not. There will be a separate SVM for each class.
Since each proposed region can have different sizes and aspect ratios but for feeding them into ConvNet which has been already trained on the large ImageNet dataset of fixed dimensions(if you are using pretrained network as your feature extractor) then you must have to change the size of each regions into the one on which the network has been trained on. for this we use Image warping method, you can check it out here

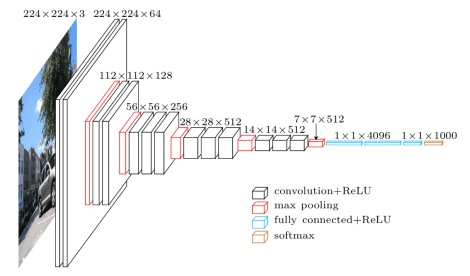
Transfer Learning :
There are various Networks which has been trained on large image datasets like VGG , ResNet , AlexNet , Inception-ResNet , Dense-Net e.t.c (shown above). If you are using such type of pre-trained networks in your model for the feature extraction process then you must fine tune it so that it can adapt to your datasets requirement.However the learning rate in this case must be very low (say 0.0001) to not to disturb the learned parameters that much.
You have to change the output layers of such network with your own layer with C+1 nodes in it (C represent no. of classes and 1 representing the background class).Once the network has been fine tuned the extracted feature can be directly fed to the classifier.
Choosing positive and negative examples:
There is a difference in choosing positive examples during fine tuning of ConvNet and SVM classifier.
During Fine tuning we want our network to extract rich features for our proposed regions hence in that case positive features will be selected among the regions proposed by the segmentation process which will be decided by the threshold value of IOU discussed above
Whie in SVM classifier training we want our model to classify the images into their separate class having high accuracy which can be generalised to all types of images containing that class so we use the ground truth example as the positive example for each class.
Bounding Box regression:
The bounding box around the proposed region due to the segmentation isn’t accurate .It can crop out some of the parts of the object , to correct the accuracy of the bounding box we use a linear regression method to learn a function which maps the proposed region bounding box into the ground truth bounding box.
A bounding box is composed by 4 parameters (x,y,w,h) first two represent the coordinate of the centre and the last two represent width and height of the box respectively.

Tech report (v5)
Ross Girshick Jeff Donahue Trevor Darrell Jitendra Malik
UC Berkeley
References:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1311.2524.pdf
http://islab.ulsan.ac.kr/files/announcement/513/rcnn_pami.pdf